Real-Time Data
At a simple level, a radio frequency identification (RFID) system consists of an RFID tag that emits a radio signal and a device that picks up the signal. The device that receives the analog signal is called an RFID reader, which produces electricity that runs down its cable at a particular rate. When the electricity reaches a piece of metal on the reader’s antenna, the antenna radiates the same signal out in space at a certain frequency and wavelength. After generating the outgoing signal, the RFID reader “listens” for a response from the RFID tag, which has its own antenna from which to transmit this response.
The tags referred to here are of the passive type, meaning that they do not have their own power supply and must rely on the signal emitted from the reader in order to transmit data back to the reader. Active RFID tags, on the other hand, have an onboard power supply (e.g., a battery), and they are constantly emitting signals (provided that the battery is not dead, of course). For a more in-depth discussion of the differences between active and passive RFID tags, refer to Passive RFID Tags vs. Active RFID Tags.
Types
RFID readers can differ based on configuration: they can be handheld, fixed (stationary), or mounted.
Handheld

Handheld readers are typically used to locate items in distribution centers or to read tags that do not go through RFID portals. These wireless, battery-powered readers are convenient and versatile. Some are self-contained computers, while others can be attached to handheld computers made by a variety of manufacturers.
Fixed

Stationary RFID readers can be affixed to walls, doorways or other types of portals, and tables/desktops. As tagged items pass through the portal (or by the table or desk), the reader picks up the tags’ data, which are then stored in a database. The database is updated in real-time, making RFID a powerful technology for use in asset tracking and inventory management applications.
Mounted
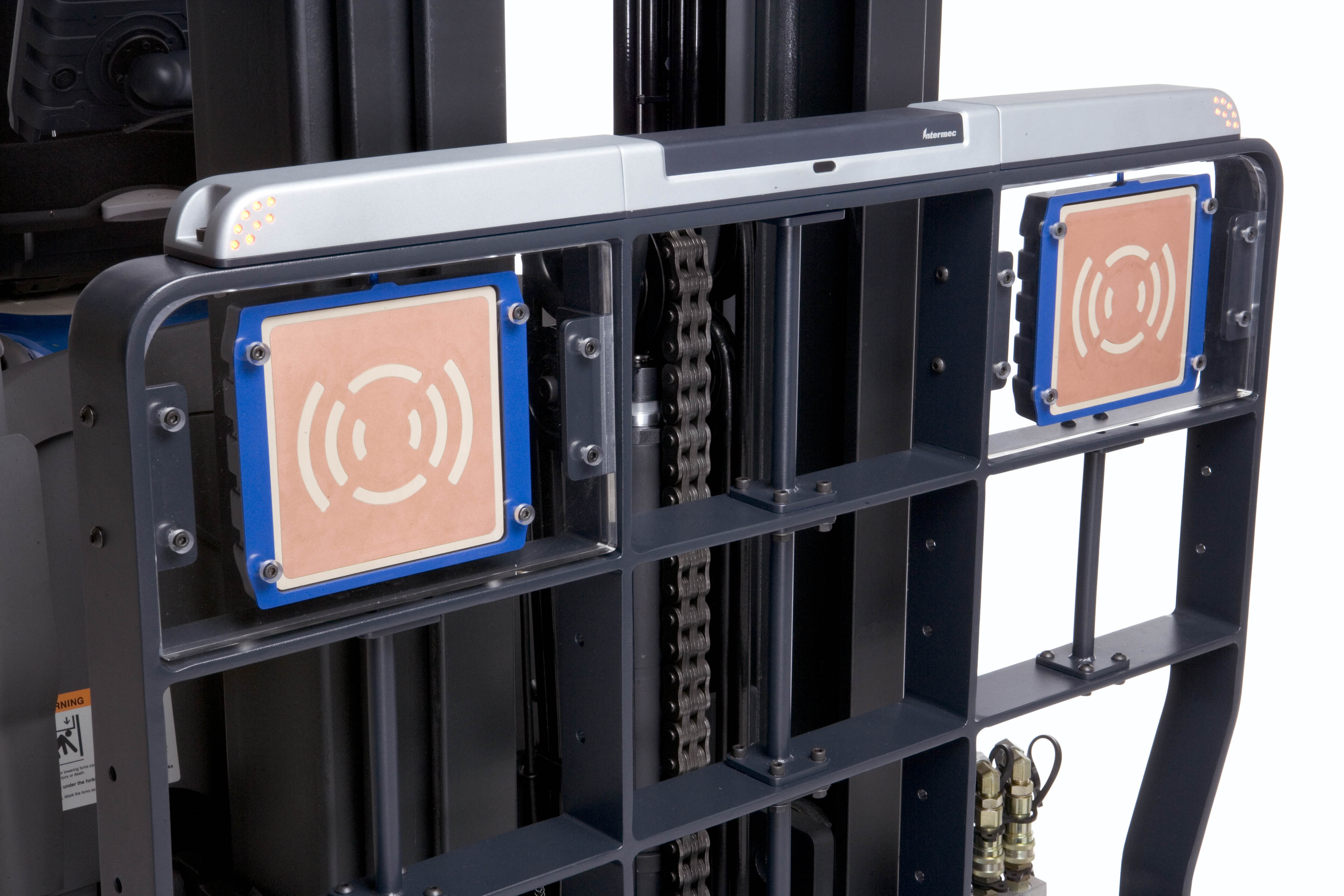

Mounted readers are used on trucks or forklifts, and they keep track of the movement of items from one location to another. Mounted RFID readers read the tags attached to the items, cases, or pallets that the vehicle is carrying. The locations of the readers themselves can be determined by interfacing the readers with tags embedded in the ground or mounted on walls throughout the facility. Mounted readers can operate in either autonomous mode; reading tags and immediately sending their data to the database host or interactive mode; where the reader stores data for a specified length of time before they are uploaded to the database.
Antennas
An RFID Reader can have one antenna or several


It is not limited to reading data from a tag; it can also write data to the tag. Performance features used to characterize RFID readers are:
- Read range: the distance at which all of the tags in use can be read
- Read rate: the number of tags that can be read per second
- Write range: the distance at which unique identifying information can be encoded on all of the tags in use by the particular application
- Write rate: the number of tags that can be encoded per second
- Identification range: the distance at which all of the RFID tags in use can be identified
Have questions about RFID Solutions? Leave us your contact information and we’ll be happy to help you!
Solving challenges and making it work for your business is our #1 priority.
AB&R®’s Solution Process
Phase I
Solution Design
During this phase our experts will:
- Perform an in-depth discovery to learn more about your specific requirements & conduct a professional technical assessment.
- Test & validate various hardware, software, and tags/labels, as applicable, to identify ones that will achieve your optimal solution.
- Develop & deliver your Solution Design Specification (SDS): proving our recommendations and detailing the budgeting costs and process we will use to implement your solution.

Phase II
Solution Implementation
During the second phase our experts will:
- Upon your agreement, acquire the selected equipment, software, supplies, and services in your SDS. We will install, configure & calibrate to ensure the solution works to your expectations.
- Confirm your acceptance of the installation, configuration, training, transition, validation, and support, validating that we have met your data-driven expectations for the performance and quality of the implemented solution.

Customer Experience
Ongoing
Continued communications will include:
- Customer feedback requests on your experience with AB&R – we want it to be the best experience.
- Quarterly Review meetings to discuss progress, success, outstanding issues that may need further assistance, and ways to further maximize your return on your investment.
AB&R®’s goal is to provide you with an efficient operation that maximizes ROI. Our solution process has been refined over the years to ensure we keep this promise for every customer.
Blog Posts
Read the latest blogs on Professional Services & Solutions
-
-
-
Barcode and RFID technology and automation
I. Declare. War. No, this isn’t a thumb war or even a battlefield by any means. However, we see numerous companies livin...
03 April, 2019